Filament 3D Printing
Filament 3D Printing (FDM) or sometimes also known as FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication), is the most well-known and widespread printing methodology, especially in the hobbyist sector.
At Treddy, we offer this technology at an industrial level, designed for extreme performance.
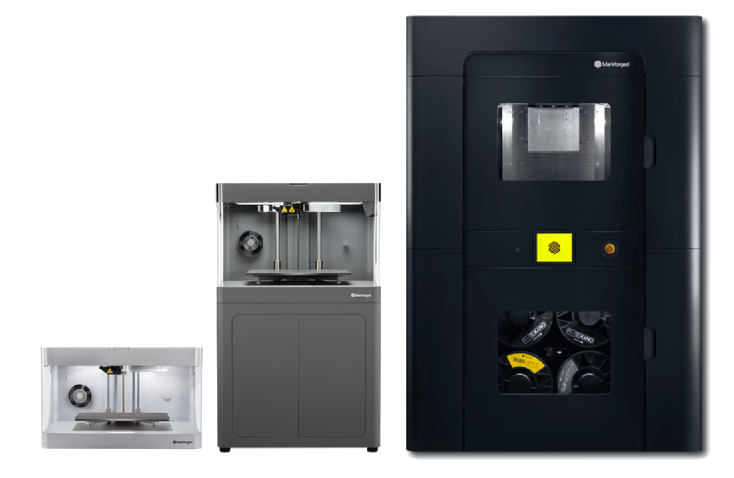

Which advantages does FDM offer?
High Performing Polymers
This technology offers a wide range of materials, including super polymers that ensure excellent mechanical performance even at very high temperatures.
Lightness
This technology offers a wide range of materials, including super polymers that ensure excellent mechanical performance even at very high temperatures.
Continuous Fiber Reinforcement (CFR)
In addition to using strong and durable materials, continuous fiber reinforcement (CFR) further enhances the strength and stiffness of the printed parts.
Available materials for LFAM

Precise PLA Multicolor

Nylon (White)

Smooth TPU (White / Black)

ULTEM
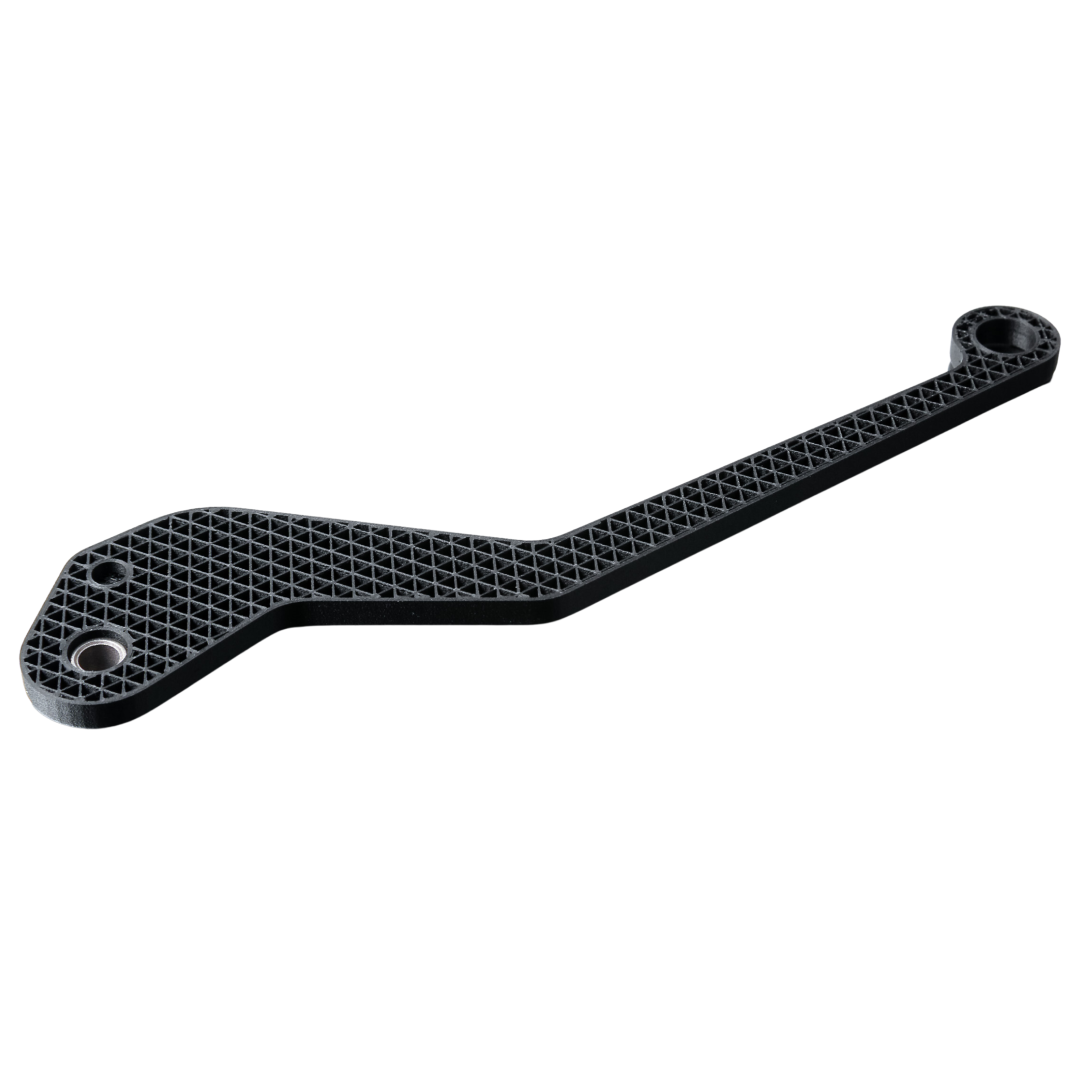

Onyx™
- Composite material Nylon 6 + Micro Carbon Fiber
- Sturdy and durable
- Toughness and resistance to chemicals
- It can be further reinforced with continuous fibers:
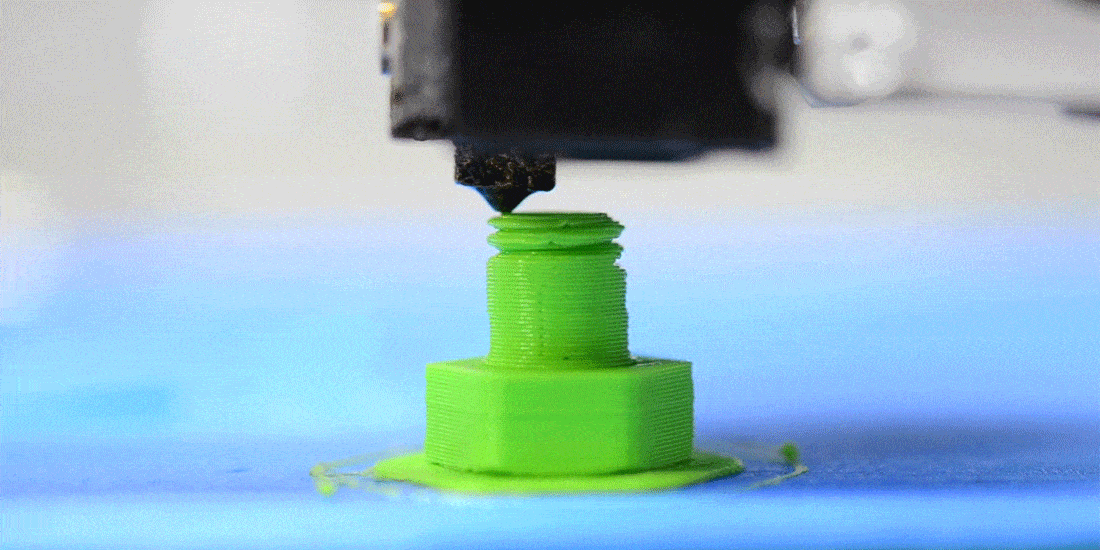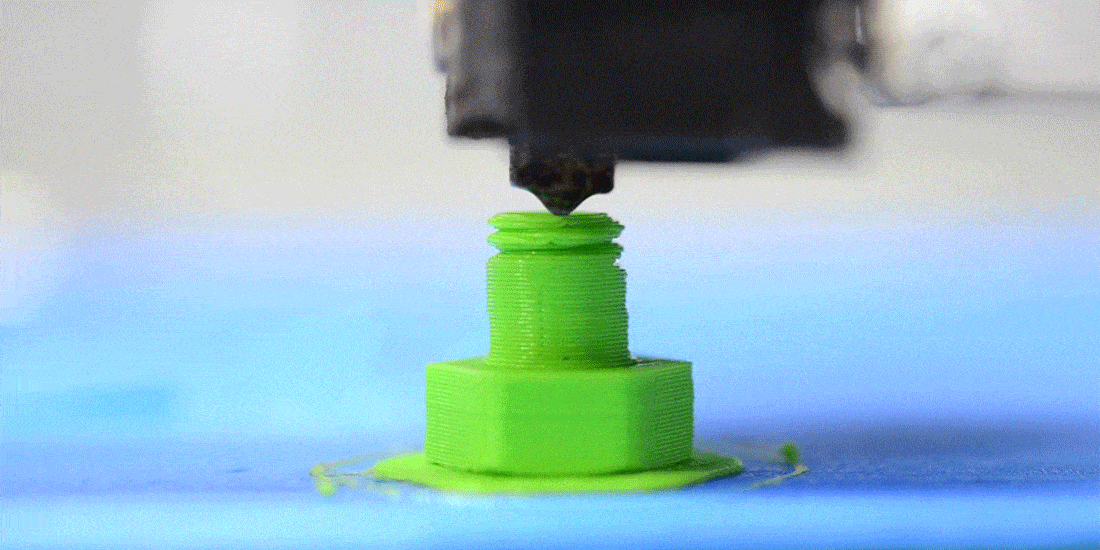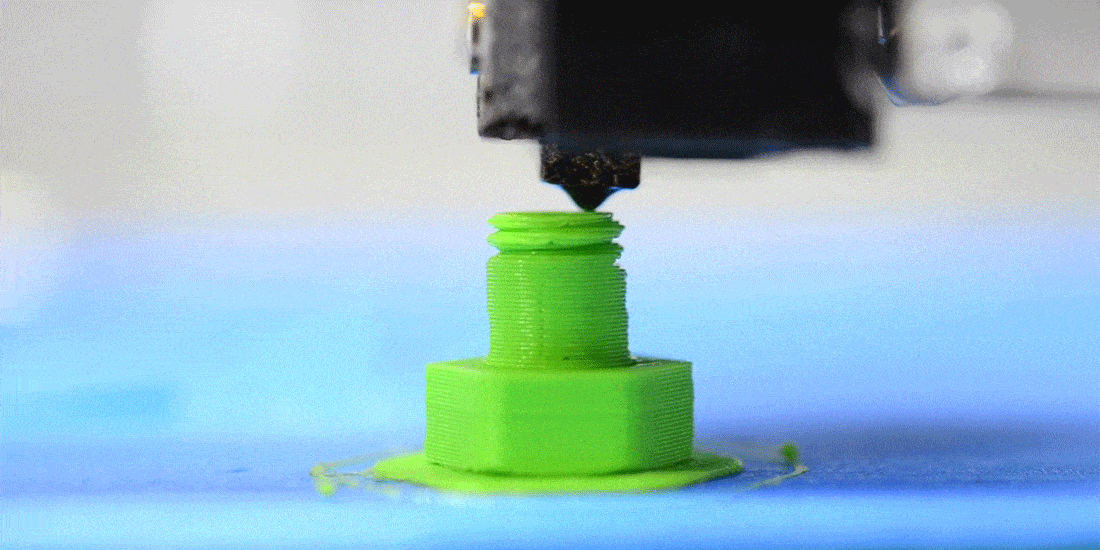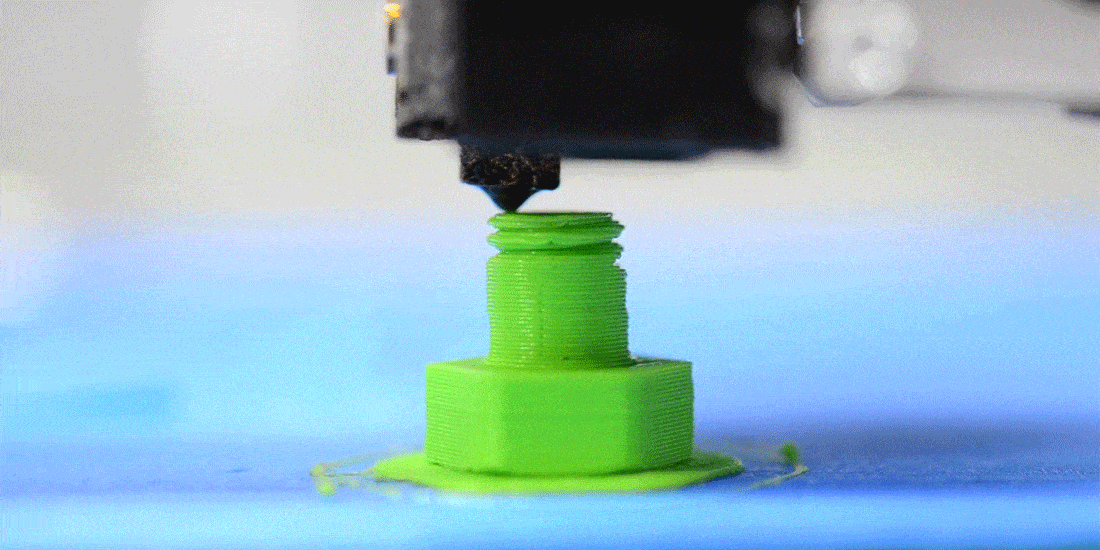
How does FDM 3D printing work?
The material in filament form is pushed into a heated nozzle. Here, the material is melted and then extruded, meaning pushed out onto the print bed.
As the print bed lowers, the nozzle and print head move horizontally to trace the contours of the object. This process is repeated layer by layer until the construction of the three-dimensional object is complete.
This technology requires supports for overhanging parts. The supports are easily removed at the end of the printing process.